The question isn’t whether you should mine Bitcoin — it’s how. In 2026, with the network hashrate surging past 800 EH/s, difficulty above 110T, and the block reward at 3.125 BTC post-halving, the economics of mining have shifted dramatically. For the home miner and the pleb miner alike, the decision between hosting your machines at a professional facility and running them yourself at home has never been more consequential.
At D-Central Technologies, we’ve been in the trenches since 2016. We’ve built miners, repaired thousands of ASICs, hosted machines in Quebec, and helped hundreds of Canadians set up home mining operations. We’ve seen both models succeed — and both fail — depending on circumstances. This is the honest, no-hype breakdown from the Bitcoin Mining Hackers.
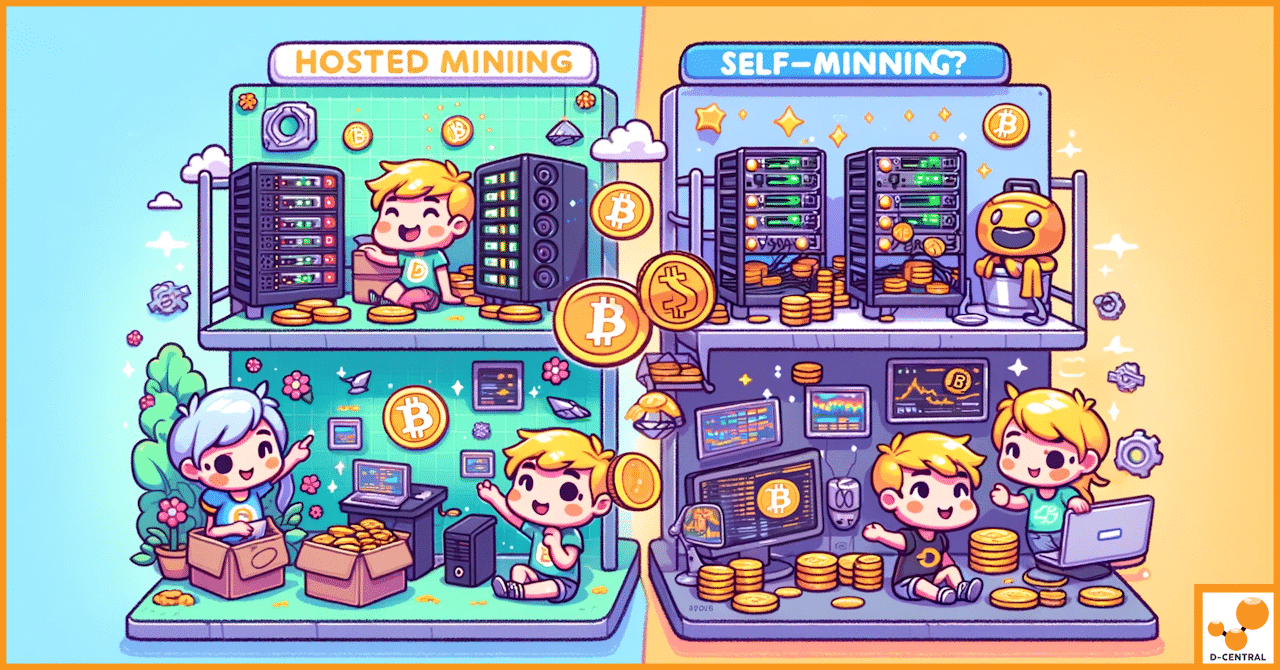
What Hosted Mining Actually Means in 2026
Let’s be precise about terminology. Hosted mining (also called colocation mining) means you own the hardware but pay a facility to rack, power, cool, and monitor it. This is fundamentally different from cloud mining (where you rent hashrate you don’t control — often a scam). With hosting, your ASIC miner sits in a professionally managed data center, and you keep the Bitcoin it earns minus hosting fees.
How Hosting Works at D-Central
D-Central’s hosting facility is located in Laval, Quebec — strategically positioned to leverage Quebec’s abundant, affordable hydroelectric power. Quebec consistently offers some of the lowest industrial electricity rates in North America, often between $0.04-0.06 CAD/kWh depending on contract structure. That’s a massive advantage when electricity is the single largest ongoing cost in any mining operation.
When you host with D-Central, here’s what you get:
| Service | What’s Included |
|---|---|
| Power | Stable Quebec hydro electricity, metered per machine |
| Cooling | Industrial-grade ventilation and cooling infrastructure |
| Monitoring | 24/7 uptime monitoring, automated alerts |
| Physical Security | Secured facility with controlled access |
| Maintenance | Basic hardware checks and issue escalation |
| Network | Redundant internet connectivity, optimized for mining pools |
You own the machine, you choose the pool, you receive the sats. D-Central handles the infrastructure. It’s a clean division of responsibilities.
Self-Mining at Home: The Sovereign Approach
Self-mining means running ASICs or open-source miners in your own space — your garage, basement, spare room, or dedicated mining shed. For Bitcoiners who value sovereignty above all else, this is the purest form of mining. Your keys, your hardware, your hashrate, your rules.
In the early days, this meant tolerating jet-engine noise levels and sweltering heat. In 2026, the game has changed completely.
The Home Mining Revolution
Three developments have transformed home mining:
1. Open-source solo miners like the Bitaxe. The Bitaxe family — Supra, Ultra, Hex, Gamma, GT — lets anyone run a solo miner on their desk for under $100 in power per year. You’re not going to heat your house with a Bitaxe, but you’re contributing to decentralization and taking your shot at a full 3.125 BTC block reward. Every hash counts.
2. Bitcoin Space Heaters. D-Central’s Bitcoin Space Heaters are repurposed ASIC miners enclosed in custom housings that function as legitimate space heaters. An S9 Space Heater Edition pushes ~1,400W of heat into your living space while mining Bitcoin. During a Canadian winter, that heat isn’t wasted — it’s replacing your electric baseboard heater. Your effective mining cost drops to near zero because you were going to spend that electricity on heating anyway.
3. Noise and heat management solutions. Custom shrouds, duct adapters, and purpose-built enclosures have made it practical to run full-size ASICs at home without losing your sanity or your spouse.
What You Need for Home Mining
| Component | Solo (Bitaxe) | Home ASIC (Space Heater) | Serious Home Farm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware Cost | $50-300 | $500-2,000 | $5,000-50,000+ |
| Power Draw | 5-15W | 1,000-1,500W | 3,000-15,000W+ |
| Electrical Work | Standard outlet | Standard 15A circuit | Dedicated circuits, possibly 240V |
| Noise Level | Silent | Moderate (enclosed) | High — needs isolation |
| Heat Output | Negligible | Space heater equivalent | Requires dedicated ventilation |
| Technical Skill | Beginner | Intermediate | Advanced |
The Real Cost Comparison: Hosting vs. Self-Mining
Let’s cut through the theoretical and look at the actual numbers that matter. We’ll compare three scenarios for running a modern mid-range ASIC miner (approximately 100 TH/s at 3,000W) over 12 months.
Scenario 1: Hosted at D-Central (Quebec Hydro)
| Cost Category | Annual Estimate (CAD) |
|---|---|
| Hardware (you own it) | $2,500-4,000 (one-time) |
| Hosting fees (power + service) | $2,400-4,200/year |
| Maintenance/repairs | Included in basic monitoring |
| Your involvement | Minimal — check dashboard, collect sats |
Scenario 2: Self-Mining at Home (Ontario/Average Canadian Rates)
| Cost Category | Annual Estimate (CAD) |
|---|---|
| Hardware | $2,500-4,000 (one-time) |
| Electricity ($0.10-0.18/kWh residential) | $2,600-4,700/year |
| Cooling/ventilation setup | $200-1,000 (one-time) |
| Noise mitigation | $100-500 (one-time) |
| Your involvement | Active — monitoring, maintenance, troubleshooting |
Scenario 3: Self-Mining With a Bitcoin Space Heater (Canadian Winter Offset)
This is where the math gets interesting. If you’re running a Bitcoin Space Heater during heating season (roughly October through April in most of Canada — 7 months), the electricity cost of the miner replaces your heating bill rather than adding to it.
| Cost Category | Annual Estimate (CAD) |
|---|---|
| Hardware (Space Heater edition) | $500-2,000 (one-time) |
| Electricity (7 months heating offset) | Net ~$0 during heating season |
| Electricity (5 summer months, full cost) | $1,000-2,000 (or shut down in summer) |
| Effective annual power cost | $1,000-2,000 (40-60% savings vs. year-round) |
The Space Heater approach is particularly devastating in a Canadian context. We have long winters, expensive heating, and a cultural willingness to run machines that make noise in the basement. It’s almost like this country was designed for Bitcoin mining.
Beyond Dollars: The Factors That Actually Matter
Profitability spreadsheets are necessary but not sufficient. The hosted vs. self-mining decision involves dimensions that don’t fit neatly into a calculator.
Sovereignty and Custodial Risk
When you mine at home, your hashrate is sovereign. Nobody can unplug your machine except you (and maybe your local utility). With hosted mining, you’re trusting a third party with physical custody of your hardware. What happens if the hosting company goes bankrupt? What if they get raided? What if they quietly redirect your hashrate?
These aren’t paranoid hypotheticals — the history of Bitcoin mining is littered with hosting companies that disappeared overnight. D-Central has been operating since 2016 with a physical facility you can visit in Laval, Quebec. Longevity and transparency matter. But even with a trustworthy host, the sovereign miner at home accepts less counterparty risk.
Decentralization of Hashrate
This is where ideology meets practicality. Every home miner running their own machine contributes to geographic and political decentralization of Bitcoin’s hashrate. Large hosting facilities, even good ones, represent concentrations of hashpower that could theoretically be pressured by regulators.
The cypherpunk case for home mining is clear: the more hashrate distributed across thousands of home miners, the more resilient Bitcoin becomes. This is why D-Central builds and sells home mining hardware alongside offering hosting services — because decentralization is the mission, not just a marketing line.
Noise, Heat, and Domestic Harmony
Let’s be honest. A full-size ASIC miner at ~75 dB is louder than a vacuum cleaner running 24/7. If you live in an apartment, a condo, or a house where your family has opinions about constant industrial noise, home mining with a full ASIC may not be viable without serious investment in sound isolation.
This is where hosted mining shines for urban miners. Ship your machine to D-Central’s Quebec facility, let it roar in an industrial building designed for the purpose, and enjoy silent sats at home.
Alternatively, the Bitaxe line operates nearly silent — perfect for a desk, shelf, or bedside table. You won’t heat your house with it, but you’ll run a sovereign solo miner without anyone in your household noticing.
Technical Capability and Maintenance
ASICs break. Hashboards fail. Fans die. Power supplies degrade. If you’re mining at home, you’re also your own technician. When a hashboard goes down at 2 AM, it’s your problem.
D-Central’s ASIC repair service has fixed thousands of machines since 2016 — we know exactly how often things go wrong. If you’re comfortable with a soldering iron and diagnostic tools, home mining is deeply satisfying. If you’d rather not deal with hardware failures, hosting removes that burden.
When Hosting Wins
Hosted mining at a facility like D-Central’s in Quebec is the stronger choice when:
- You have high residential electricity costs. If you’re paying $0.15+/kWh at home, Quebec hydro rates at a hosting facility will outperform your home setup on pure economics.
- You can’t manage the noise and heat. Apartment dwellers, condo owners, or anyone without a dedicated space for loud equipment.
- You want passive income. Ship the machine, point it at your preferred pool, collect Bitcoin. Minimal ongoing involvement.
- You’re scaling up. Running 5+ ASICs at home requires serious electrical infrastructure. A hosting facility already has it.
- You travel frequently. Machines need monitoring. If you’re away from home often, hosted mining provides peace of mind.
When Self-Mining Wins
Running your own machines at home is the stronger choice when:
- You have cheap electricity. If you’re on a low residential rate, off-grid solar, or a time-of-use plan where night rates are rock-bottom, home mining can beat hosting economics.
- You value sovereignty above all else. Your hardware, your location, your rules. No counterparty risk.
- You can use the heat. This is the Canadian superpower. A Bitcoin Space Heater in a cold climate turns mining into a heating subsidy. The economics become almost unbeatable during winter.
- You enjoy the technical challenge. Building, tweaking, overclocking, repairing — for the maker community and hardware enthusiasts, this is the point.
- You want to contribute to hashrate decentralization. Every home miner makes the network stronger. That matters.
The Hybrid Approach: Why Not Both?
Here’s what the smartest miners in our community do: they run both. A Bitaxe or two on the desk for sovereign solo mining. A Bitcoin Space Heater in the basement for winter heat offset. And their newest-generation ASIC hosted at D-Central’s Quebec facility for maximum hashrate with professional infrastructure.
This hybrid approach gives you:
- Income diversification across different cost structures
- Sovereignty (home miners) plus efficiency (hosted miners)
- Contribution to hashrate decentralization
- A hedge against any single point of failure
It’s not either/or. The best answer for many miners is “yes, and.”
D-Central: Your Partner for Either Path
Whether you choose to host with us in Quebec or mine from your home, D-Central supports the full lifecycle:
- Hardware sales — From Bitaxe solo miners to full-size ASICs and Bitcoin Space Heaters
- Mining hosting — Professional colocation at our Laval, Quebec facility
- ASIC repair — Thousands of machines repaired since 2016, model-specific expertise
- Mining consulting — Help choosing the right setup for your situation
- Mining training — Learn to maintain and optimize your own machines
We don’t push one model over the other because we believe in the mission: decentralization of every layer of Bitcoin mining. The more miners running — at home, at our facility, anywhere in the world — the stronger Bitcoin becomes.
We are the Bitcoin Mining Hackers. We take institutional-grade technology and hack it into accessible solutions for the home miner, the garage miner, the basement miner, and the pleb who refuses to let corporations own all the hashrate.
Every hash counts.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is hosted mining the same as cloud mining?
No, and this distinction is critical. With hosted mining (colocation), you own the physical hardware — it just sits in someone else’s facility. You control which pool to mine on, and you receive the Bitcoin directly. Cloud mining means you’re renting hashrate from a company, often with no way to verify the hardware even exists. Cloud mining has a long history of scams in the Bitcoin space. Hosted mining with a reputable, established company like D-Central (operating since 2016 with a physical facility in Laval, Quebec you can visit) is a fundamentally different and more transparent arrangement.
What is the break-even period for a home mining setup in 2026?
It depends heavily on your electricity rate, the hardware you choose, and the current Bitcoin price and network difficulty. With a modern mid-range ASIC (~100 TH/s) at $0.10 CAD/kWh, break-even is typically 12-18 months at current Bitcoin prices. With a Bitcoin Space Heater where you’re offsetting heating costs during Canadian winters, break-even can come significantly faster — sometimes under 8-10 months for the heating season portion. Use the D-Central Mining Profitability Calculator to model your specific scenario with current difficulty (110T+) and the 3.125 BTC block reward.
Can I visit my hardware at D-Central’s hosting facility?
Yes. D-Central’s hosting facility is located in Laval, Quebec (4479 Desserte Nord Autoroute 440, Laval, QC H7P 6E2). We believe in transparency — your machines are real, they’re running, and you can verify it. Facility visits can be arranged by contacting us in advance. This is one of the advantages of hosting with a Canadian company that has a real physical presence, not an anonymous data center in an undisclosed location.
What happens to my hosted miner if D-Central goes out of business?
You own the hardware, so it’s your property regardless of what happens to the hosting company. In any hosting agreement, ensure you understand the terms for hardware retrieval. D-Central has been operating continuously since 2016 — one of the longest-running Bitcoin mining companies in Canada — and our facility in Quebec is a real, accessible location. That said, counterparty risk is inherent in any hosted arrangement, which is why many of our customers run a hybrid setup: some machines hosted with us and some running at home for sovereignty.
Should a complete beginner start with hosting or home mining?
For someone brand new to Bitcoin mining, we recommend starting with a Bitaxe solo miner at home. It costs under $100 in hardware, uses about 15W of power (pennies per month), runs silently, and teaches you the fundamentals of mining — pool configuration, hashrate monitoring, wallet setup — without any risk. Once you understand the basics and want more hashrate, you can decide whether to scale up at home (perhaps with a Bitcoin Space Heater for winter) or host a larger ASIC at D-Central’s Quebec facility. Starting small at home, then expanding based on experience, is the smartest path.