Antminer S15 Maintenance & Repair Guide
Table of Contents
The Antminer S15 is a Bitcoin mining device developed by Bitmain and launched in December 2018. It features a 7nm ASIC chip and offers two operating modes: high-performance mode and energy-saving mode.
In high-performance mode, the device can deliver a maximum hashrate of 28 trillion calculations per second, while in energy-saving mode, it consumes less power. The Antminer S15 has a power consumption of 1600W, meaning it uses 1600 watts of electricity during operation.
This guide is designed to assist you in setting up, maintaining, and resolving any issues that may arise with your Antminer S15. It provides detailed instructions and troubleshooting tips to ensure that your device is functioning optimally, whether you are new to Bitcoin mining or an experienced miner.
(VID)
Preparation and Maintenance Guidelines
It’s essential to take the time to properly prepare and maintain components before, during, and after installation. This includes applying thermal paste for better heat transfer, forming air ducts for better airflow, connecting power supplies in the correct sequence, fixing chips to prevent overheating, and ensuring test fixtures meet production requirements. Additionally, these guidelines should also include instructions on cleaning components with approved solvents such as isopropyl alcohol or distilled water, as well as how to store components away from extreme temperatures and humidity levels safely. Finally, regularly scheduled maintenance checks should be carried out every few months or at least annually to guarantee the proper functioning of all parts within the system.
Preparation Requirements for Repair Platform, Tools, and Equipment
I. Platform Requirements
- The requirements for the platform include a workbench for repairing Antminer S15 hashboards that must be properly grounded. In addition, an anti-static wrist strap and grounding are also required to prevent static electricity from damaging the materials being worked on.
II. Equipment Requirements
- Thermostat soldering iron at 350-450 degrees Celsius, pointed solder tip for small patches like r-c.
- Heat gun for chip disassembly and soldering, no long-time heating in case of PCB blistering.
- APW3 power source with 12V and 133A Max output to test the hash board.
- Multimeter, tweezer, S15 hash board tester (oscilloscope preferred).
- Scaling powder, cleaning water and anhydrous alcohol; cleaning water is used to clean the residue and appearance after maintenance.
- Tin grinder, tin stencils, and solder paste; implant tin for chips upon renewals.
- Heat-Conducting Glue, black (3461), to glue the cooling fin after maintenance.
III. Test Tool Requirements
ARC Kit
- ARC Antminer Hashboard Tester
- Lab PSU 10-30V / 1-15A
Bitmain Kit
- APW9+ power supply and power patch cord for hash board power supply
- Use the test fixture of the V2.3 control board (test fixture material number ZJ0001000001).
IV. Maintenance Auxiliary Materials/Tools Requirements
- Solder Paste 138°C, flux, Mechanic lead-free circuit board cleaner, and anhydrous alcohol.
- Mechanic lead-free circuit board cleaner cleans up the flux residue after maintenance.
- Thermally conductive gel is used to apply to the chip surface after repair.
- Ball-planting steel mesh, desoldering wick, and solder balls (the recommended ball diameter is 0.4mm).
- When replacing a new chip, it is necessary to tin the chip pins and then solder them to the hash board. Apply thermally conductive gel evenly on the chip’s surface, then lock the heatsink.
- Serial port code scanner.
- Serial port adapter board RS232 to TTL adapter board 3.3V.
- Self-made short-circuit probe (use the pins for wiring and welding and heat the shrinkable sleeve to prevent short-circuit between the probe and the small heatsink).
V. Common Maintenance Spare Material Requirements
- 0402 resistor (0R, 10K, 4.7K,)
- 0402 capacitor (0.1uF, 1uF)
Maintenance Requirements
- Maintenance personnel should have good knowledge of electronics, at least one year of experience, and a strong mastery of QFN encapsulation and soldering techniques.
- Check the maintenance work at least twice, and ensure the result is satisfied each time.
- Pay close attention to the techniques used during maintenance, ensure no obvious PCB deformation after changing fittings, and check for missing/open circuits and short circuits on parts.
- Check the maintenance target, corresponding test software parameters, and the hash board tester.
- Check the tools and testers.
How to use a miner tester fixture
A miner tester fixture is a device that can help you test the hash boards of your Antminer S15 and detect any damaged chips. To use it, you need to follow these steps:
- Unzip the files the test fixture supplier provided and copy them to the root directory of a TF card.
- Insert the TF card into the test fixture and turn on the power. Wait for about 2 minutes until the indicator light flashes.
- Take out the TF card and insert another containing the test file matching your miner hash board model. You can download these files from online sources.
- Connect the test fixture to your computer with a USB cable and open the software. Create a new connection and configure the parameters correctly.
- Connect your hash board to the test fixture with a voltage regulator line. For some models, you may need to use your miner’s power supply to power the test fixture.
- Start testing your hash board and check for errors or faults on the software interface.
Overview of Antminer S15 Components
Antminer S15 Hashboard Structure
The Antminer S15 is a robust mining machine that comprises 12 voltage domains connected in series, with each domain consisting of 5 BM1391 chips, resulting in a total of 60 BM1391 chips on the board. These chips have three built-in small voltage domains connected in series, making them highly efficient. The BM1391 chip requires a 25M monocrystal oscillator on the clock, which is connected in series and passes from the first chip to the last chip. The S15 has small cooling fins on each chip’s front and back that operate independently. During maintenance, the cooling fins must be fixed with black heat-conducting glue evenly distributed on the back of the IC. The power supply of the S15 is APW8, which is regulated by the control panel. The APW8 will not output without a control panel to regulate the voltage; the typical voltage is 220V. These features make the Antminer S15 T15 a reliable and efficient mining machine.
Boost Circuit of S15 Hashboard
The 23V boost circuit is a component that increases the voltage from 19.2V to 23V for DC-DC applications. This is achieved by using a switching power supply, U7, which produces a switching signal. The energy storage inductor, L4, stores this energy and charges and discharges C73-C75 through boost rectifier diode, D4. The resulting voltage is then filtered by EC26 to obtain the 23V voltage at its positive electrode. This 23V voltage is output to U170, which outputs 1.8V and then 0.8V through U171. Overall, the circuit boosts the voltage from 19.2V to 23V for use in DC-DC applications.
The signal direction of S15 chips
- The CLK signal flow is represented by the color red and is produced by the Y1 25M crystal oscillator. This signal is transmitted from the No. 1 chip to the No. 60 chip. During standby and computing, the voltages for both states are 0.9±0.1V.
- The TX (CI, CO) signal flow, also represented by red, is transmitted from IO mouth pin 7 in the No. 00 chip to the No. 62 chip. The voltage is 0V when the IO signaling wire is not plugged in and 1.8V during computing.
- The RX (RI, RO) signal flow is represented by the color yellow and returns from the No. 60 chip to the No. 00 chip before returning to the control panel through IO mouth pin 8. The voltage is 0V when the IO signaling wire is not plugged in and 1.8V during computing.
- The B (BI, BO) signal flow, also represented by red, lowers the electrical level from the No. 00 chip to the No. 60 chip. The voltage is 0V when the IO signaling wire is not plugged in or during standby, and the signal impulse is approximately 0 during computing.
- Lastly, the RST signal flow, represented by red, is transmitted from IO mouth pin 3 in the No. 00 chip to the No. 62 chip. The voltage is 0V when the IO signaling wire is not plugged in or during standby, and 1.8V during computing.
Introduction to the S15 miner and its components
The S15 miner is composed of several components, each of which plays a crucial role in the mining process. These components include the miner itself, the power supply unit (PSU), the cooling fans, and the control board. The miner itself houses the mining chips and performs the hashing calculations that are necessary for mining cryptocurrencies. The PSU provides the necessary power to run the miner, while the cooling fans ensure that the miner stays at an optimal temperature to avoid overheating. The control board is responsible for managing and coordinating the various components of the miner, ensuring that they work together smoothly and efficiently.
Definition of IO pins
The IO port of the S15 T15 hash board consists of a 90-degree in-line dual row of 18 pins with a 2X9 pitch of 2.0 PHSD.
- Pins 5, 6, 17, and 18 are ground pins.
- Pins 15 and 16 (SDA, SCL) are used for the I2C bus of DC-DC PIC, allowing communication between the control board and the PIC—the IC at U6-EPROOM stores PCB, BOM, and chip information.
- Pin 13 (PLUG0) is the identification signal of the hash board. When the IO signal is inserted, the pin should be high.
- Pins 11, 12, and 14 (A2, A1, A0) are the PIC address signals connecting to U6-EPROOM.
- Pins 7 and 8 (TXD, RXD) are used for the hashrate channel at the end 3.3 of the hash board. They become signals TX (CO) and RX (RI) after being divided by a resistor.
- Pin 3 (RST) is the reset signal on the 3.3V terminal, which becomes a 1.8V RST reset signal after being divided by a resistor.
- Pin 4 (D3V3) supplies power at 3.3V to the hash board, provided by the control board to provide working voltage to the PIC.
Testing and Troubleshooting
Testing points for chips and how to test them
To test the functionality of the Antminer S15 hash board’s chips, there are five test points labelled TP1, TP2, TP3, TP4, and TP5. A multimeter measures the resistance between each test point and the ground. A normal resistance value of around 10 ohms is expected, and any deviation from this value suggests a possible chip failure in that particular voltage domain. During an overhaul, ten tests are conducted before and after the main test chip, including five tests before and after the chip. The testing process involves supplying power to the control board and measuring the voltage at each test point, including CLK, CO, RI, BO, and RST. The testing method helps to identify any abnormal test point statuses or voltages, and the fault point can be estimated based on the circuit before and after the test point. The pins for the BM1391 chip, including CLK, TX, RX, BO, and RST, are connected to specific input and output pins, and the testing process helps to identify any issues with these connections.
Troubleshooting common Antminer S15 failures
The Antminer S15 is an ASIC miner that is highly efficient and capable of mining various cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin. However, like any other electronic device, it may experience some common problems that can affect its performance or operation. External factors such as grounding, electric leakage, network issues, or dust accumulation can cause some issues, while internal factors like fan failure, chip failure, firmware corruption, or miner settings can also cause problems. To troubleshoot these issues, you can check the miner’s status indicators, kernel logs, hash rate, and temperature. Additionally, you may need to reset the miner to factory settings or reload the firmware. In some cases, you might need to replace the fan or hash board. If the issue is complex, you can send the miner to a professional repair center for repair.
Heat sink displacement
The Antminer S15 features independent small cooling fins on both the front and back of each chip. These cooling fins help to dissipate the heat generated by the chips and maintain them within a normal temperature range. However, under certain circumstances, such as poor adhesion, vibration, or transportation, the cooling fins may fall off, which can cause heat sink displacement and adversely impact the miner’s performance or stability. To prevent this problem, it is essential to regularly inspect the miner for any fallen heat sinks or components. Additionally, it is vital to handle the miner with care and avoid shaking it too vigorously. If you find any heat sink displacement, it is recommended to contact a professional repair center for assistance.
Voltage-domain voltage imbalance
Voltage-domain voltage imbalance is a condition where the voltage values of different voltage domains on a hash board of the Antminer S15 are not equal. In this case, a voltage domain refers to a group of chips that share a common power supply. The Antminer S15 has 12 voltage domains on each hash board, and each domain contains six chips. The voltage between the voltage domains is 1.53V, and the voltage value of the first and last voltage domain is 18.36V. This condition can adversely affect the performance and stability of the miner and may indicate underlying issues in the hash board, such as faulty chips or poor soldering. It is essential to address voltage-domain voltage imbalance promptly to ensure the miner operates efficiently and without issue.
Missing chips
Missing chips on the Antminer S15 is a problem that arises when some chips on the hash board are not detected or are not functioning correctly. This issue can lead to low hashrate or abnormal temperature readings. Missing chips can be caused by various factors, such as a faulty power supply, poor grounding, damaged fan cable, bad soldering, or defective chips. One way to identify missing chips is by checking the miner status page log, where it will show the number of chips detected on each hash board. To fix missing chips, you may need to replace the power supply, ensure good cables and grounding, reset the miner to its factory setting, or replace the hash board altogether. It is crucial to address missing chips promptly to ensure that the miner operates efficiently and without issue.
Broken chain
A broken chain on the Antminer S15 is a problem that arises when one or more hash boards are not connected correctly to the control board. This issue can result in low hashrate or no hashrate at all. Broken chain can be caused by various factors, such as loose cables, faulty connectors, damaged control board or hash board. One way to identify a broken chain is by checking the miner status page, where it will show the number of hash boards detected and working. To fix a broken chain, you may need to ensure good cables and connectors, reload the firmware, reset the miner to its factory settings, or replace the control board or hash board. It is crucial to address a broken chain promptly to ensure that the miner operates efficiently and without issue.
Failure to run
Failure to run on the Antminer S15 is a problem where the miner fails to start normally, does not hash, or has an unstable hashrate. This issue can result in loss of mining revenue or damage to the miner. Failure to run can be caused by various factors, such as grounding problems, electric leakage, network issues, firmware problems, power supply unit (PSU) problems, or hash board problems. One way to identify failure to run is by checking the log on the miner status page, where it will show any errors or warnings. To fix failure to run, you may need to ensure good grounding, network, and power supply, reload firmware, reset the miner to its factory settings, or replace faulty components. It is important to address failure to run promptly to ensure that the miner operates efficiently and without issue.
Hashing boards not being detected
Hashing boards are the components of Antminer S15 that perform the actual mining operations. Sometimes, one or more hashing boards may not be detected by the miner, which can affect its performance and efficiency. There are several possible causes and solutions for this problem:
- The flat cable that connects the hashing board to the control board is damaged or loose: power off the miner, re-plug the flat cable or replace it with a new one.
- The firmware of the miner is corrupted: power off the miner, reset it by pressing the IP Reporter button for 10 seconds, and then upgrade it to the latest firmware version.
- The hashing board is damaged: check if there are any visible signs of damage on the board, such as burnt chips or capacitors. If so, request for warranty repair or use a test fixture to pinpoint and replace the faulty components.
- The control board is damaged: check if there are any visible signs of damage on the board, such as burnt chips or capacitors. If so, request for warranty repair or replace it with a new one.
Low hashrate
A low hashrate on Antminer S15 means that the miner is not performing at its optimal level and is producing less mining rewards than expected. There are several possible causes and solutions for this problem:
- The miner is running in low power mode: this mode reduces the power consumption and noise of the miner, but also lowers its hashrate. To switch to normal mode, go to Miner Configuration > Advanced Settings > Frequency > select Normal Mode > Save & Apply.
- The miner is overheating: high temperature can affect the performance and stability of the miner. To prevent overheating, make sure the miner is well ventilated, clean the fans and heat sinks regularly, and avoid direct sunlight or other heat sources.
- The network connection is unstable: poor internet connection can cause delays or errors in mining. To improve the network connection, use a high-quality Ethernet cable, check your router settings, and avoid network congestion or interference.
- The firmware is outdated: old firmware may have bugs or compatibility issues that affect the hashrate. To update the firmware, go to System > Upgrade > select a file from your computer or a URL > Flash image.
Fan failure
Fan failure on Antminer S15 means that one or more of the fans that cool down the miner are not working properly or at all. This can cause overheating, low hashrate, or miner shutdown. There are several possible causes and solutions for this problem:
- The fan connector is loose or damaged: power off the miner, check if the fan connector is plugged all the way into the socket and there’s no damage on the fan cable. If there is any damage, replace the fan with a new one.
- The fan speed is too low or too high: power off the miner, check if there is any dust or debris on the fan blades that may affect its rotation. Clean the fan with a soft brush or compressed air. If the problem persists, replace the fan with a new one.
- The control board is faulty: power off the miner, swap the front and rear fans and see if the problem follows the fan or stays with the control board. If it stays with the control board, request for warranty repair or replace it with a new one.
- The firmware is corrupted: power off the miner, reset it by pressing the IP Reporter button for 10 seconds, and then upgrade it to the latest firmware version.
Temperature lower or higher than normal
If the temperature is lower than normal, it may indicate that the device is not working properly or that the ambient temperature is too cold. If the temperature is higher than normal, it may indicate that the device is overheating or that the ambient temperature is too hot. In either case, it is advisable to check the device for any faults or dust accumulation, and to monitor the intake air temperature with an ethernet temperature sensor. Excessive temperatures can damage the device and reduce its lifespan.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Proper cleaning and maintenance are crucial for maintaining the optimal performance and efficiency of the Antminer S15. Here are some steps to follow for cleaning and maintenance:
- Use an air gun to gently blow the front and rear fans twice. Be careful not to touch the grille or fan blades to prevent damage. Blow every gap for 2-3 seconds and repeat 2-3 times.
- Use a soft brush or cotton swab to remove any dust or dirt from the heat sinks, chips, cables, and connectors. Avoid using any liquids or metal tools that may cause corrosion or short circuits.
- Regularly check the cables for any wear and tear and replace them as necessary. Always use fireproof electrical and network cables in your setup.
- Inspect the hash boards frequently for any faults or damage. Use a test fixture to examine each voltage domain and chip on the hash board. If any issues are found, contact Bitmain support for repair guidance.
- Regularly upgrade the firmware to fix any bugs or improve performance. You can download the latest firmware from Bitmain’s website.
- If you encounter any system issues, consider resetting or restoring the miner to its factory settings. You can also use an SD card to recover the miner if it fails to boot up.
Following these steps will help ensure that your Antminer S15 runs smoothly and efficiently, allowing you to maximize your mining output while minimizing any downtime or damage.
How to remove dust from the miner
- Disconnect the power supply and allow the miner to cool down.
- Use a soft-bristled brush to remove dust from the fan blades and heatsinks gently.
- Avoid using water or cleaning solutions as they can damage the electronics.
- Use compressed air or a vacuum cleaner on a low setting to blow or suck out the remaining dust.
- Take care not to touch any of the electronic components while cleaning.
- Reassemble the Antminer S15 and plug it back in.
- Regular cleaning and maintenance of the Antminer S15 will help to extend its lifespan and ensure it operates efficiently.
Fan replacement procedures
- Power off the Antminer S15 and unplug it from the power source.
- Remove the screws that secure the top cover of the miner and remove the cover.
- Locate the faulty fan and unplug its connector from the control board.
- Use a screwdriver to remove the screws that secure the fan to the heatsink or bracket.
- Carefully remove the faulty fan from the miner, not damaging electronic components.
- Take the new fan and align it with the screw holes on the heatsink or bracket.
- Secure the new fan to the heatsink or bracket using the screws you removed earlier.
- Reconnect the fan’s connector to the control board, ensuring it’s properly seated.
- Replace the top cover of the Antminer S15 and secure it using the screws that you removed earlier.
- Plug the miner back into the power source and turn it on to confirm that the new fan works correctly.
Firmware and Software Upgrades
Firmware and software upgrades on Antminer S15 are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and functionality of the device. These upgrades improve the stability of the miner, enhance its performance, and provide new features and functionality. Firmware upgrades typically address bugs and vulnerabilities, provide improved security measures, and increase the overall efficiency of the miner. Failing to upgrade your Antminer S15’s firmware and software can lead to reduced performance, increased downtime, and potential security risks. Therefore, it’s crucial to regularly check for and install any available firmware and software upgrades to keep your Antminer S15 operating at its best.
How to upgrade firmware and software
- Access the Antminer S15’s web interface by entering the miner’s IP address into your web browser.
- Navigate to the “System” tab and select “Upgrade.”
- Choose to upgrade the firmware, software, or both.
- Select the appropriate file for the upgrade, which you can download from the manufacturer’s website or other trusted sources.
- Click “Upgrade” to begin the process and allow it to complete.
- After the upgrade, the Antminer S15 will automatically reboot to apply the changes.
- Avoid interrupting the power supply to the miner during the upgrade process to prevent damage.
- Regularly upgrade the firmware and software of your Antminer S15 to ensure optimal performance and stability.
How to use an SD card for recovery
If you’re experiencing problems with your Antminer S15 Miner due to missing programs, you can use an SD card to flash the firmware and potentially resolve the issue. You’ll need a MicroSD card with a recommended capacity of less than 16GB, a computer running Windows XP or later, and a card reader.
- Recommended tools for flashing firmware on Antminer S15 Miner using an SD card include a MicroSD card (less than 16GB), a computer with Windows XP or later, and a card reader.
- Download the firmware image from the manufacturer’s website and follow the flashing instructions carefully.
- Depending on your control board model, you may need to shift the JP4 jumper or short-circuit the AB to enable flashing using the SD card.
- After flashing, power off the control board, reset the jumper or AB to the original position, and reboot the miner.
- If you encounter any issues during the flashing process, try reformatting the TF, ensuring that the firmware is correct, cleaning the TF, or trying with a different SD card.
- If you cannot resolve the issue, contact the manufacturer or reseller for further support.
How to reset the miner to factory settings
- Access the Antminer’s Configuration Interface
- Connect your Antminer S15 to your computer or laptop via an Ethernet cable
- Open a web browser and enter the Antminer’s IP address into the address bar
- Log in to the Configuration Interface
- Enter your login credentials
- The default username and password are both “root”
- Navigate to the “System” Tab
- Click on the “System” tab located at the top of the page
- Click “Factory Reset”
- In the “System” tab, you should see an option labelled “Factory Reset.”
- Click on it
- Confirm the Reset
- You’ll be prompted to confirm the reset
- Click “OK” to confirm
- Wait for the Reset to Complete
- The Antminer S15 will automatically restart and perform a factory reset
- This process may take several minutes, so be patient
- Log in to the Configuration Interface Again
- Once the reset is complete, you’ll need to log back into the Antminer’s configuration interface using the default username and password (“root”)
- Configure the Antminer S15
- After resetting your Antminer S15 to its factory settings, you’ll need to reconfigure it to your preferences, such as setting the pool URL, username, and password and configuring your network settings
Other Considerations and Maintenance Flow Chart
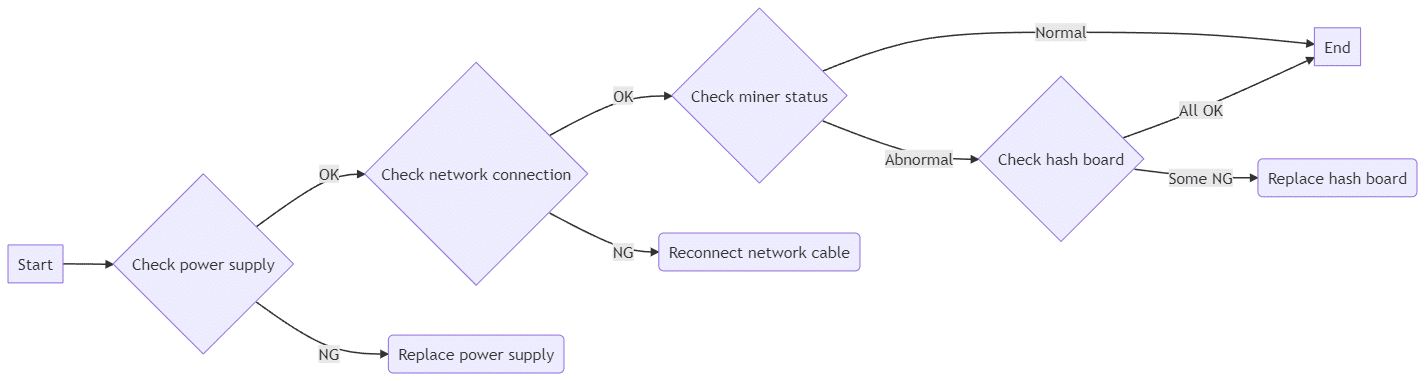
Additional maintenance considerations
- The routine maintenance for Antminer S15 involves several steps. Firstly, visually inspect the hash board for any small heatsink shift deformation. If any issues are found, the small heat sink should be shifted, the original gum removed, and the heat sink repaired and re-glued. Secondly, the impedance of each voltage domain should be checked for short or open circuit conditions. If any issues are discovered, they must be adequately handled. Lastly, voltage detection should be carried out for each voltage domain, ensuring the voltage difference does not exceed 0.05. If a voltage field has a voltage that is too high or too low, this could indicate an abnormality in the circuit of its adjacent voltage field. Troubleshooting the cause of the abnormality is necessary.
- After routine testing, checking for any short circuits to prevent damage to chips or other materials when the board is energized is essential. A chip detection test box is available to determine the location of the faulty chip based on the test box detection results. Display the test box detection results and start locating the faulty chip, checking its test points (CLK IN OUT/TX IN OUT/RX IN OUT/B IN OUT/RST IN OUT) and ensuring equal voltage for VDD, VDD 0V8, VDD 1V8, and VDD 2V5.
- Signal flow should be inspected to locate the faulty chip. Reverse transfer of the RX signal (723-1 Number Chip) and forward delivery (1-72) of several signals, including CLK, CO, BO, and RST, must be checked in the power supply sequence point to identify any abnormal faults. If the faulty chip is located, it must be re-welded. This involves adding flux around the chip, heating the solder points of the chip pin until they dissolve, and gently moving the chip left and right before pressing it. This enables the chip pin to re-attach to the pad and collect the tin, achieving the effect of re-tin. If the fault persists after re-welding, the chip can be replaced directly.
- After repairing the hash board, it must be tested more than twice using a test box. The first test should be done after replacing the faulty parts and allowing the board to cool down. Once the test is passed, leave the board aside. The second test should be carried out once the hash board has wholly cooled down after a few minutes. Although these two tests may take a few minutes, they do not delay the overall repair time. Once the second board is repaired and cooled, the first board should be tested again. This staggered approach enables more efficient use of time.
- Once the hash board is repaired, it is necessary to classify the fault and record the replacement component model, location, reasons, and other relevant details. This information can be used for feedback to production, after-sales support, or research and development. After recording the information, the repaired hash board can be reinstalled into the whole miner for regular testing.
Disclaimer: The information provided on this blog is for informational purposes only and should not be taken as any form of advice.
Ready to become an ASIC expert?
The D-Central team is a well-established and recognized authority in matters of ASIC repair. Our Training Course is tailored to equip individuals with the skills they need to tackle even the toughest repair jobs with confidence. The consulting services we offer provide our clients with expert guidance and support, allowing them to get the most out of their repair sessions. By bringing their own equipment, participants can learn to fix up to five broken devices during each session, making the trip pay for itself. Don’t let technical details hold you back.






