Today, we uncover a hidden threat to the efficiency and longevity of mining operations: oxidation. Often overlooked, oxidation significantly impacts the performance of the essential hashboards that power the mining process. In this blog, we’ll delve into the deadly connection between oxidation and hashboard performance, shedding light on how this seemingly innocuous process can wreak havoc on mining efficiency, leading to lower hash rates, increased power consumption, and a shorter lifespan for these crucial components. Join us as we uncover the facts about this silent menace and discuss strategies for mitigating its harmful effects on your Bitcoin mining endeavours.
Oxidation: The hidden enemy of Bitcoin Mining
Oxidation is a chemical reaction when a substance loses electrons, often due to exposure to oxygen or other oxidizing agents. Although it might seem unrelated to Bitcoin mining at first glance, this hidden enemy can severely impact the performance of mining equipment, particularly the vital hashboards for maintaining efficient mining operations.
The oxidation process affects metals in various ways, depending on the type of metal and the oxidizing agent involved. Common consequences include the formation of rust on iron or steel surfaces and tarnish on copper or silver components. These reactions weaken the metal structures and can significantly alter their electrical properties, such as conductivity and resistance. Metals are typically good conductors of electricity due to the free electrons in their structure. However, when metals oxidize, these free electrons are transferred to the oxidizing agent, decreasing the number of available electrons for conducting electric current. This, in turn, increases the resistance of the metal, leading to reduced efficiency and higher power loss.
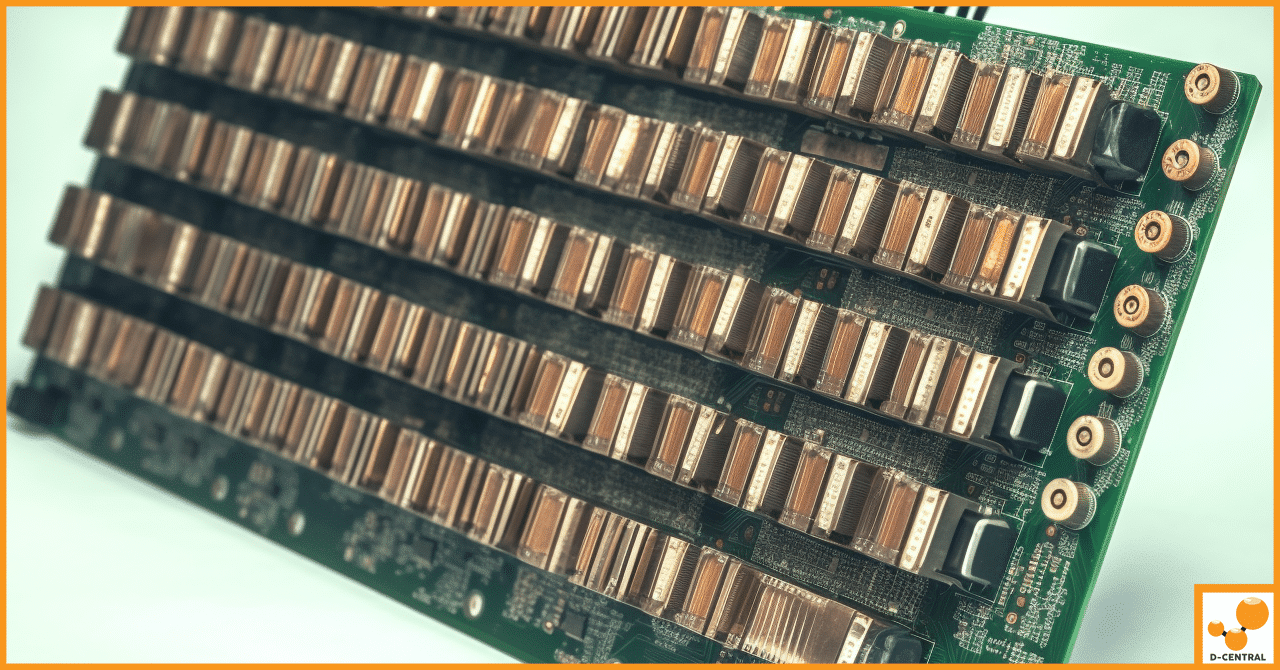
In Bitcoin mining, hashboards consist of several metal components, such as wires, connectors, chips, capacitors, resistors, and transistors. These components are essential for the functioning of the hashboards, as they facilitate communication, computation, and power supply for the ASICs (application-specific integrated circuits) responsible for performing the complex calculations required to mine Bitcoin. Unfortunately, these metal components are also susceptible to oxidation, particularly when exposed to high temperatures, humidity, dust, or dirt. Oxidation can damage these components by causing rust, tarnish, or other corrosion forms, impairing their performance and functionality by reducing conductivity and increasing resistance. The result is a decline in hash rates, increased power consumption, and a shorter lifespan for the hashboards.
The critical role of hashboards in Bitcoin mining
Hashboards play a crucial role in the process of Bitcoin mining. They are circuit boards that house the ASICs (application-specific integrated circuits) responsible for performing the SHA-256 hashing algorithm required to mine Bitcoin blocks. The ASICs on the hashboards carry out complex computations to solve mathematical problems, validate transactions, and secure the blockchain. As miners successfully solve these problems, new blocks are added to the blockchain, and the miners are rewarded with newly minted bitcoins. Consequently, the performance and efficiency of hashboards are directly linked to the profitability of a mining operation.
Despite their critical function, hashboards are highly susceptible to oxidation, severely impacting their performance and lifespan. Hashboards consist of various metal components, such as wires, connectors, chips, capacitors, resistors, and transistors, which are vital to the functioning of the ASICs. These components enable communication, computation, and power supply for the ASICs, but their metal makeup makes them vulnerable to oxidation, particularly when exposed to high temperatures, humidity, dust, or dirt.
Oxidation can damage these components by forming rust, tarnish, or other corrosive substances, affecting their electrical properties, such as conductivity and resistance. As conductivity decreases and resistance increases, the hashboards’ performance declines, resulting in lower hash rates, higher power consumption, and a shorter lifespan. This degradation in performance can have significant implications for the profitability and sustainability of Bitcoin mining operations. Therefore, understanding the impact of oxidation on hashboards and implementing measures to prevent or reduce oxidation is vital for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of Bitcoin mining equipment.
The deadly effects of oxidation on hashboard performance
Oxidation has several deadly effects on the performance of hashboards, which can significantly undermine the efficiency and profitability of Bitcoin mining operations. One of the most prominent consequences is the reduction in hash rates. As oxidation affects the electrical properties of the metal components, such as conductivity and resistance, the ASICs on the hashboards become less efficient in performing the SHA-256 hashing algorithm. Lower hash rates mean a decreased likelihood of successfully mining new blocks, leading to reduced rewards for the miner.
Another detrimental impact of oxidation on hashboards is increased power consumption. As the electrical resistance of the metal components rises due to oxidation, more energy is required to maintain the same level of performance. This heightened power consumption escalates the operational costs of Bitcoin mining and exacerbates the environmental concerns associated with the energy-intensive process.
Lastly, oxidation considerably shortens the lifespan of hashboards. The damage inflicted upon the metal components by rust, tarnish, and other corrosive substances weaken their structure, making them more prone to malfunction or failure. Over time, this degradation results in the need for more frequent repairs or replacements of hashboards, adding to the overall costs and reducing the sustainability of Bitcoin mining operations.
In summary, the deadly effects of oxidation on hashboard performance manifest as lower hash rates, higher power consumption, and a shorter lifespan. These consequences directly impact the profitability and viability of Bitcoin mining, underscoring the importance of understanding and mitigating oxidation risks to maintain efficient and sustainable mining operations.
Tin whiskers: A related hazard in Bitcoin mining hashboards
Tin whiskers pose another significant hazard in Bitcoin mining hashboards. These whiskers are thin, hair-like filaments of tin that can grow from surfaces where tin is used as a final finish, such as solder joints or plating. Tin whiskers form due to compressive stress within the tin layer, which factors like thermal expansion and contraction, mechanical pressure, or internal grain structure changes can cause.
The presence of tin whiskers can have a severely negative impact on hashboard performance. They can cause short circuits or electrical noise by bridging closely-spaced circuit elements, compromising the integrity of the electrical signals. Furthermore, tin whiskers can break off and migrate to other parts of the hashboard, creating additional problems and potentially damaging the ASIC chips. These issues can lead to decreased hashing performance, contributing to the inefficiency and unprofitability of Bitcoin mining.
Several preventative measures can be taken to mitigate the formation of tin whiskers in Bitcoin mining hashboards. One approach is to avoid using pure tin or tin-rich alloys for soldering or plating; instead, opt for metals or alloys less prone to whisker formation, such as lead, silver, or nickel. Another strategy involves applying a protective coating or sealant over the tin layer to prevent oxygen and moisture from reaching it and causing oxidation. Finally, reducing thermal and mechanical stress on hashboards can help prevent tin whiskers; this can be achieved by using proper cooling systems and avoiding the over-tightening of screws or bolts. Implementing these preventative measures can help maintain the reliability and performance of hashboards in Bitcoin mining operations, reducing the risk of failures associated with tin whiskers.
Thermal stress: Another contributing factor to hashboard issues
Thermal stress is yet another contributing factor to hashboard issues in Bitcoin mining. To understand thermal stress, it’s important first to grasp the concepts of thermal expansion and contraction. When a material is heated, its molecules vibrate faster and move farther apart, causing the material to expand. Conversely, when a material is cooled, its molecules vibrate slower and move closer together, causing it to contract. Thermal stress occurs when a material is subjected to temperature changes while being constrained, resulting in the exertion of force on the material by the constraint, which subsequently leads to strain or deformation.
Thermal stress plays a significant role in the degradation of hashboards. Fluctuating temperatures can lead to the expansion and contraction of the materials used in the hashboards and ASIC chips, creating microcracks or gaps that allow moisture and oxygen to penetrate and cause oxidation. This oxidation can further increase stress within the components, eventually resulting in damage or failure. Moreover, when the hashboards are exposed to high temperatures for extended periods, the solder joints and bonding wires may weaken, compromising their structural integrity and increasing the risk of delamination or other performance issues.
Managing thermal stress is crucial to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of hashboards in Bitcoin mining operations. Proper cooling systems must maintain stable temperatures and prevent overheating to achieve this. Additionally, materials with low coefficients of thermal expansion or high moduli of elasticity can be used to minimize the impact of temperature changes on the hashboards. Implementing thermal insulation or cooling systems to control temperature fluctuations and designing hashboards with expansion joints or gaps for free movement of materials can also help reduce thermal stress-related issues. By effectively managing thermal stress, Bitcoin miners can extend the lifespan and enhance their mining hardware’s performance, ultimately increasing their operations’ efficiency and profitability.
Chips delamination in 17 series Antminers: An example of oxidation’s impact
Chips delamination in 17 series Antminers is a prime example of oxidation’s negative impact on Bitcoin mining hardware. Delamination occurs when the chips on the hashboard separate from the substrate due to thermal stress or mechanical shock, leading to malfunctions or complete failure of the chips. This can result in a lower hashrate, missing hashboards or chips, and issues with reading temperature sensors.
Several factors contribute to chip delamination in 17 series Antminers. High temperature and humidity, particularly in certain regions during winter, can cause thermal expansion and contraction of the hashboard and chips, creating cracks or gaps that allow moisture and oxygen to penetrate and cause oxidation. This oxidation further increases stress within the chips, ultimately leading to delamination. Additionally, mechanical shock or vibration during transportation or installation can damage the solder joints or bonding wires between the chips and the substrate, weakening their adhesion and making them more prone to delamination.
Strategies for protecting hashboards from oxidation and other issues
Protecting hashboards from oxidation and other issues is crucial to ensure the longevity and efficiency of Bitcoin mining equipment. Implementing various strategies can help minimize the risk of oxidation and maintain optimal hashboard performance.
Firstly, cooling systems and dehumidifiers can help maintain a stable and appropriate environment for the miners. Proper temperature and humidity control can reduce the likelihood of thermal stress, expansion, and contraction, leading to cracks and oxidation in the long run.
Secondly, conducting regular maintenance and inspection of the mining equipment is essential. By routinely examining the hashboards for signs of damage, oxidation, or other issues, miners can identify potential problems early on and take corrective action before the situation worsens. This proactive approach can extend the lifespan of the hashboards and ensure that the mining operation runs smoothly.
Lastly, firmware upgrades and optimization can play a significant role in protecting hashboards from oxidation-related issues. Updated firmware or custom software can offer better temperature and fan speed control, preventing overheating and reducing the risk of thermal stress. Optimization through overclocking or undervolting can also help balance performance and power consumption, allowing miners to achieve maximum efficiency while minimizing the risk of hardware damage due to oxidation or other factors.
By adopting these strategies, Bitcoin miners can effectively safeguard their hashboards from oxidation and other issues, ensuring optimal performance and longer service life for their mining equipment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the deadly connection between oxidation and hashboard performance is a critical concern for Bitcoin miners. Oxidation can lead to reduced hash rates, increased power consumption, and a shorter lifespan for hashboards, ultimately impacting mining operations’ overall efficiency and profitability. Miners must understand the threats of oxidation and related issues, such as tin whiskers and thermal stress, and take appropriate measures to mitigate these risks.
By implementing strategies like proper cooling and dehumidification, applying anti-corrosive coatings, conducting regular maintenance and inspection, and optimizing firmware, miners can effectively combat oxidation and protect the longevity and performance of their hashboards. Taking these steps will help ensure the smooth operation of Bitcoin mining equipment and contribute to the long-term success and sustainability of the entire mining ecosystem. Addressing oxidation and its associated challenges is essential for maintaining efficient and profitable Bitcoin mining operations in an increasingly competitive market.
FAQ
Q: What is the connection between oxidation and hashboard performance in Bitcoin mining?
A: Oxidation is a chemical reaction that can significantly impact the performance of mining equipment, particularly the essential hashboards for maintaining efficient mining operations. Oxidation can damage metal components of hashboards, such as wires, connectors, chips, capacitors, resistors, and transistors, by causing rust, tarnish, or other corrosion forms, impairing their performance and functionality by reducing conductivity and increasing resistance. This results in a decline in hash rates, increased power consumption, and a shorter lifespan for the hashboards.
Q: What are the deadly effects of oxidation on hashboard performance?
A: The deadly effects of oxidation on hashboard performance include:
- Lower hash rates resulting from reduced electrical conductivity and increased resistance, which in turn decreases the likelihood of successfully mining new blocks.
- Higher power consumption due to increased electrical resistance, escalating operational costs and exacerbating environmental concerns.
- A shorter lifespan for hashboards as oxidation weakens their metal components, leading to more frequent repairs or replacements and reducing the sustainability of Bitcoin mining operations.
Q: What are tin whiskers and how do they impact hashboard performance in Bitcoin mining?
A: Tin whiskers are thin, hair-like filaments of tin that can grow from surfaces where tin is used as a final finish, such as solder joints or plating. They can cause short circuits or electrical noise by bridging closely-spaced circuit elements, compromising the electrical signal’s integrity. Furthermore, tin whiskers can break off and migrate to other parts of the hashboard, creating additional problems and potentially damaging the ASIC chips. These issues can lead to decreased hashing performance, contributing to the inefficiency and unprofitability of Bitcoin mining.
Q: Why is thermal stress a contributing factor to hashboard issues in Bitcoin mining?
A: Thermal stress occurs when a material is subjected to temperature changes while being constrained, resulting in the exertion of force on the material and causing strain or deformation. Fluctuating temperatures can lead to expansion and contraction of the materials used in the hashboards and ASIC chips, creating microcracks or gaps that allow moisture and oxygen to penetrate and cause oxidation. This oxidation can further increase stress within components, resulting in damage or failure. Moreover, high temperatures can also weaken solder joints and bonding wires, compromising their structural integrity and increasing the risk of delamination or other performance issues.
Q: What strategies can be implemented to protect hashboards from oxidation and other issues?
A: Strategies for protecting hashboards from oxidation and other issues include:
- Proper cooling and dehumidification to maintain a stable environment and reduce thermal stress.
- Conducting regular maintenance and inspections to identify and address potential problems early on.
- Optimizing firmware with updates or custom software that offers better temperature and fan speed control to prevent overheating and reduce the risk of thermal stress-related hardware damage. Implementing these strategies can help safeguard hashboards, ensuring optimal performance and longer service life for mining equipment.