
Harnessing Bitcoin Miners’ Heat to Boost Profits for Commercial Laundries
Welcome to a revolutionary intersection of two distinct yet surprisingly synergistic industries: Bitcoin Mining and Commercial Laundries. This exploration into
4479 Desserte Nord Autoroute 440, Laval, QC H7P 6E2

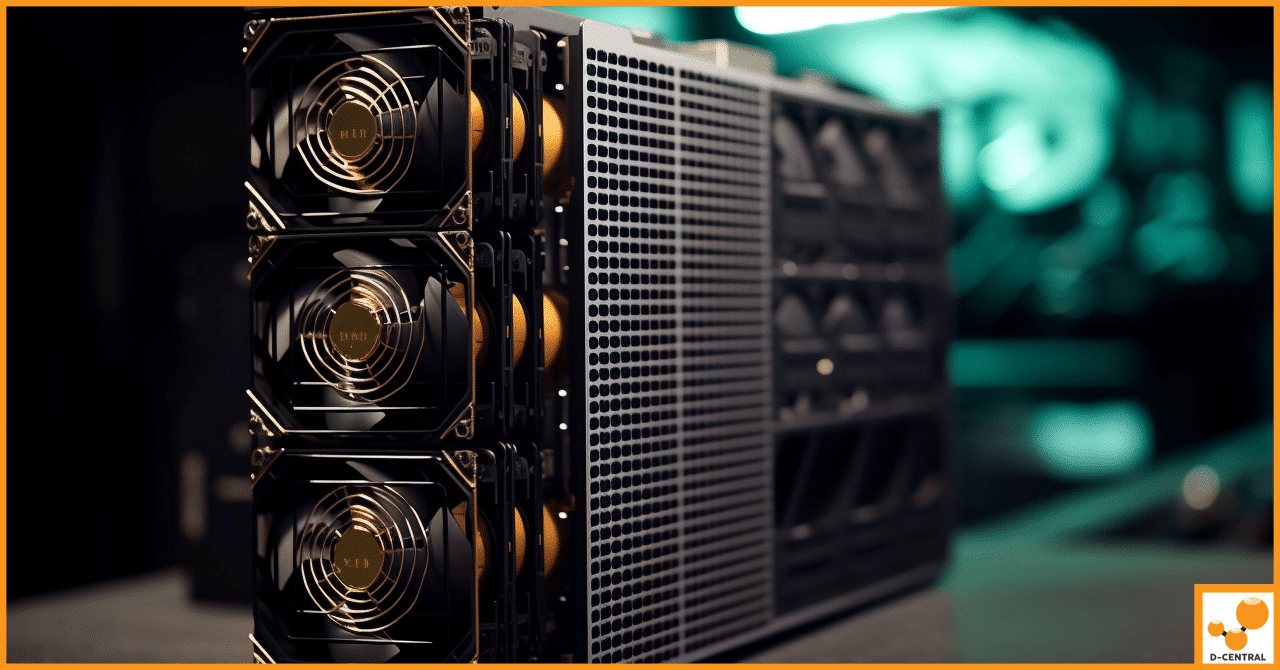
In the dynamic world of cryptocurrency, ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) miners stand as the linchpins of Bitcoin mining, a process pivotal to the functioning and security of the Bitcoin network. These specialized devices are engineered with one goal in mind: to mine Bitcoin by solving complex cryptographic puzzles at unparalleled speeds. Their efficiency and performance outstrip that of general-purpose hardware, making them indispensable for miners aiming to achieve profitability in the competitive landscape of Bitcoin mining.
However, the high-performance capabilities of ASIC miners come with their own set of challenges, primarily related to reliability and longevity. Given their continuous operation under intense conditions, the risk of hardware failure is a significant concern, potentially leading to downtime and financial losses. This is where the critical process of burn-in testing comes into play.
Burn-in testing, a rigorous procedure within the electronics manufacturing industry, is designed to ensure the reliability and durability of electronic devices before they are deployed for everyday use. By subjecting ASIC miners to extreme stress tests and operational conditions, burn-in testing aims to weed out any potential early-life failures, thereby guaranteeing that only the most robust units are put into service. This preemptive scrutiny is not just about safeguarding the miner’s operational integrity; it’s about instilling confidence among users in the device’s ability to perform consistently over time, ensuring the miner’s contribution to the Bitcoin network remains uninterrupted.
The significance of burn-in testing extends beyond a mere quality assurance step; it embodies a commitment to excellence and reliability in the realm of Bitcoin mining. As we delve deeper into the intricacies of ASIC miners and the indispensable role of burn-in testing, it becomes evident that these processes are foundational to the sustained growth and stability of cryptocurrency mining endeavors.
Burn-in testing is a critical procedure in the electronics industry, designed to evaluate the reliability and durability of electronic components and devices before they are released into the market. This process involves subjecting the devices to prolonged periods of operation under elevated stress conditions, such as high temperatures, voltage ranges, and power cycling. The primary objective is to accelerate the aging process of the components, thereby exposing any latent defects or weaknesses that might lead to early-life failures.
The essence of burn-in testing lies in its ability to mimic the harsh conditions an electronic device might encounter throughout its lifecycle, but within a condensed timeframe. This approach is based on the “infant mortality” curve of electronic components, which suggests that if a device is going to fail, it is most likely to do so in the initial stages of its operation. By pushing the devices to their operational limits, burn-in testing effectively weeds out the weak units, ensuring that only the most resilient ones make it to the end-users.
In the context of the electronics industry, burn-in testing serves multiple pivotal roles:
In summary, burn-in testing is an indispensable tool in the electronics industry, serving as a gatekeeper to ensure that only the most reliable and robust devices make it to the market. Its role in identifying early-life failures and ensuring device reliability is crucial for maintaining high standards of quality and performance in electronic products, including the ASIC miners that are at the heart of Bitcoin mining operations.
ASIC miners, the powerhouse behind Bitcoin mining, operate in an environment that demands peak performance around the clock. These specialized devices are designed to execute complex cryptographic algorithms essential for mining Bitcoin, a process that not only requires high computational power but also subjects the hardware to continuous, intense stress. The relentless operation under such conditions exposes ASIC miners to significant risks of device failure, which can stem from various factors including overheating, component fatigue, and solder joint failures, among others.
The operational environment of ASIC miners is characterized by high temperatures and continuous heavy loads, which can precipitate the early failure of electronic components. This environment is far more demanding than that of typical consumer electronics, pushing the miners to their thermal and electrical limits. The potential for device failure in such conditions is not merely a possibility but an expectation if rigorous testing and quality assurance measures, like burn-in testing, are not implemented.
The implications of ASIC miner failures extend beyond the immediate hardware replacement costs. Downtime in mining operations can result in significant opportunity losses, given the time-sensitive nature of Bitcoin mining where every second counts towards solving a block. Furthermore, hardware failures can lead to safety risks, especially in large-scale mining operations where the cumulative heat and electrical demands are substantial.
Burn-in testing emerges as a critical preemptive measure to mitigate these risks by ensuring that ASIC miners are robust enough to withstand the rigors of continuous operation. Through burn-in testing, each miner is subjected to conditions that simulate the extreme stress it will face in real-world mining operations. This process helps in identifying and weeding out units with latent defects that could lead to premature failure under stress.
The benefits of burn-in testing for ASIC miners are manifold:
In conclusion, the necessity of burn-in testing for ASIC miners cannot be overstated. It is a vital process that not only safeguards the hardware investment but also ensures the efficiency, stability, and safety of Bitcoin mining operations. As the backbone of cryptocurrency mining, the reliability of ASIC miners is paramount, and burn-in testing plays a pivotal role in achieving this reliability.
Burn-in testing stands as a critical juncture in the lifecycle of ASIC miners, significantly influencing their performance, efficiency, and longevity. This rigorous testing process not only serves as a filter to eliminate underperforming units but also as a means to optimize the operational capabilities of ASIC miners, ensuring they deliver peak performance throughout their service life.
The primary objective of burn-in testing is to subject ASIC miners to extreme operational conditions, thereby identifying and eliminating any potential failure points. This process ensures that every miner that passes the burn-in test can withstand the intense demands of continuous Bitcoin mining operations. The immediate benefit of this selective process is the enhanced performance of the ASIC miners, as only the most robust units are deployed in mining operations. These miners are less likely to suffer from performance degradation caused by component failures, ensuring consistent hash rates and operational efficiency.
Moreover, burn-in testing allows manufacturers to identify common failure modes and address them, either through design improvements or targeted interventions. This feedback loop enhances the overall design and manufacturing process, leading to the production of more reliable and efficient ASIC miners over time.
Efficiency in Bitcoin mining is not solely about the hash rate; it also encompasses power consumption, heat management, and the longevity of the mining hardware. Burn-in tested ASIC miners, having been exposed to and survived extreme conditions, are likely to exhibit superior thermal performance and power efficiency. This is because any components that could fail under thermal stress or contribute to inefficiency are likely to have been weeded out during the burn-in process.
The longevity of ASIC miners is directly tied to their operational efficiency and reliability. Burn-in testing, by ensuring that only the most durable units are put into service, directly contributes to extending the usable life of these miners. Longer-lasting hardware means reduced need for frequent replacements, translating into cost savings and a higher return on investment for miners.
The long-term profitability of Bitcoin mining operations is intricately linked to the performance and reliability of the mining hardware. Burn-in tested ASIC miners, with their enhanced performance, efficiency, and longevity, contribute significantly to the stability and predictability of mining operations. Stable operations with minimal downtime ensure a steady stream of mining rewards, which is crucial for maintaining profitability in the competitive landscape of Bitcoin mining.
Furthermore, the reduced incidence of hardware failures leads to lower maintenance and replacement costs, directly impacting the bottom line of mining operations. The assurance of using burn-in tested hardware also allows miners to plan their operations with greater confidence, making strategic decisions about scaling and investment with a clear understanding of their hardware’s capabilities and lifespan.
The impact of burn-in testing on the performance and longevity of ASIC miners is profound, with far-reaching implications for the efficiency and profitability of Bitcoin mining operations. By ensuring that ASIC miners are capable of withstanding the rigors of continuous operation, burn-in testing lays the foundation for stable, efficient, and profitable mining endeavors. It is a testament to the importance of rigorous quality assurance processes in the high-stakes world of cryptocurrency mining, where the reliability of hardware is paramount to success.
The journey through the intricacies of burn-in testing for ASIC miners underscores its indispensable role in the realm of Bitcoin mining. This rigorous process is not merely a step in quality assurance; it is a cornerstone in ensuring the reliability, performance, and longevity of ASIC miners, which are at the heart of the cryptocurrency mining industry. By subjecting these specialized devices to extreme stress tests, burn-in testing acts as a gatekeeper, ensuring that only the most robust and efficient miners are deployed in the high-stakes environment of Bitcoin mining.
D-Central Technologies stands at the forefront of this critical process, embracing advanced burn-in testing practices with a commitment to excellence and reliability. Our dedication goes beyond merely supplying hardware; it’s about providing a foundation of trust and performance for the Bitcoin mining community. We understand that the success of mining operations hinges on the unwavering reliability of their equipment, and we are committed to ensuring that every ASIC miner we provide meets the highest standards of quality and durability.
We invite you to explore the world of ASIC miners and burn-in testing services offered by D-Central Technologies. Our website is a treasure trove of information, designed to enlighten and assist both seasoned miners and those new to the field. Whether you’re looking to understand more about the critical role of burn-in testing in ASIC miner reliability or seeking to equip your mining operation with the most robust hardware, D-Central Technologies is your trusted partner.
For those who demand the utmost in performance, reliability, and expert support, D-Central Technologies is here to elevate your Bitcoin mining operations. Contact us today to discover how our advanced burn-in testing practices and comprehensive mining solutions can empower your mining endeavors. Together, let’s harness the power of reliable, efficient ASIC miners to secure a profitable future in Bitcoin mining.
What is ASIC miner?
ASIC miner, or Application-Specific Integrated Circuit miner, is a highly specialized device engineered specifically for mining cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. These devices are optimized to solve cryptographic puzzles at unparalleled speeds, significantly outperforming general-purpose hardware in the mining landscape.
Why is burn-in testing critical for ASIC miners?
Burn-in testing is essential for ASIC miners to ensure their reliability and durability before deployment. By subjecting the miners to extreme stress tests and operational conditions, this process identifies potential early-life failures, guaranteeing only the most robust units are used in mining operations. It’s a vital step for sustaining profitability and operational efficiency in Bitcoin mining.
How does burn-in testing impact ASIC miner performance and longevity?
Burn-in testing impacts ASIC miners by enhancing their performance, efficiency, and longevity. This rigorous process weeds out any underperforming units and optimizes operational capabilities, ensuring that the miners deliver peak performance throughout their service life. It contributes to miner stability, reduced downtime, and cost savings, all of which are pivotal for the profitability of mining operations.
What are the risks associated with ASIC miner failures?
The risks of ASIC miner failures include hardware replacement costs, significant opportunity losses due to downtime in mining operations, and potential safety hazards in large-scale mining facilities. These failures can stem from overheating, component fatigue, and solder joint failures, among other factors.
How does burn-in testing benefit Bitcoin mining operations?
Burn-in testing benefits Bitcoin mining operations by enhancing the reliability and efficiency of ASIC miners, reducing the likelihood of unexpected downtimes, optimizing operational efficiency, and ensuring the safety of mining facilities. This pre-emptive measure contributes to sustainable profitability and stability of mining endeavors.
Why choose D-Central Technologies for ASIC miners and burn-in testing services?
Choosing D-Central Technologies for ASIC miners and burn-in testing services provides access to advanced testing practices, commitment to excellence, and reliability. D-Central prioritizes quality and durability, ensuring every miner undergoes comprehensive burn-in testing. This fosters a foundation of trust and performance for the cryptocurrency mining community, enhancing the efficiency and profitability of mining operations.
DISCLAIMER: D-Central Technologies and its associated content, including this blog, do not serve as financial advisors or official investment advisors. The insights and opinions shared here or by any guests featured in our content are provided purely for informational and educational purposes. Such communications should not be interpreted as financial, investment, legal, tax, or any form of specific advice. We are committed to advancing the knowledge and understanding of Bitcoin and its potential impact on society. However, we urge our community to proceed with caution and informed judgment in all related endeavors.
Related Posts

Welcome to a revolutionary intersection of two distinct yet surprisingly synergistic industries: Bitcoin Mining and Commercial Laundries. This exploration into
In the dynamic world of cryptocurrency, Bitcoin mining stands as a cornerstone activity, pivotal to the maintenance and expansion of
In the world of cryptocurrency mining, efficiency and cost-effectiveness are the keys to success. One way to achieve this is